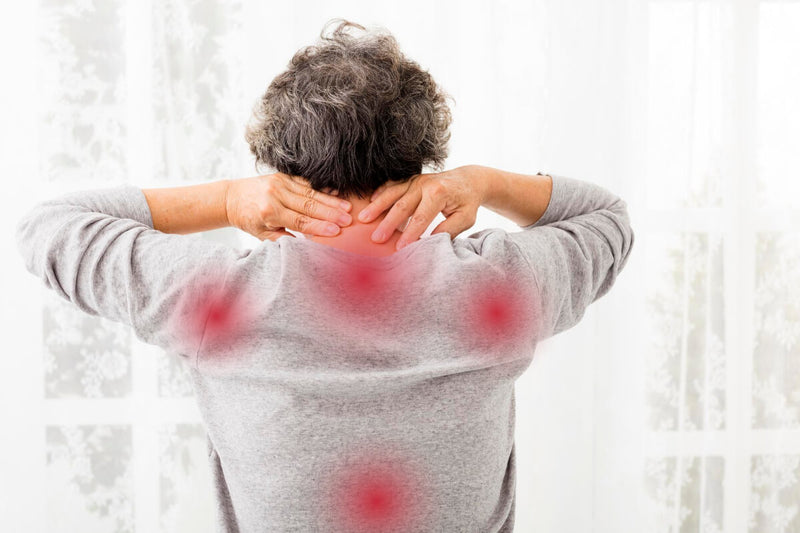
What Is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a condition that causes widespread musculoskeletal pain combined with issues of sleep, fatigue, mental, and mood disorders and issues. It affects approximately 2% of the population, approximately 4 million people in the U.S.
Fibromyalgia is frequently misdiagnosed as depression and/or anxiety because patients report similar signs and symptoms. However, fibromyalgia is a physical condition and not a mental condition that causes pain throughout the entire body.
This guide will discuss what fibromyalgia is and provide information on its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatments.
There is no cure for fibromyalgia, but you can still learn how to manage the disease and live a normal life again.

What Causes Fibromyalgia?
The exact cause of fibromyalgia and the pain it causes is not known. Doctors and researchers believe that there are multiple factors that contribute to the pain.
Some experts believe that genetics plays a role and fibromyalgia is a disease that can occur in clusters of family members.
Other possible contributors include physical trauma, emotional stressors, infections, and certain medications.
Genes
Genetics plays a large part in fibromyalgia running in families, because there are specific genes that contribute to developing fibromyalgia.
There is a theory that a genetic mutation of the pain receptors in the brain has made them more sensitized to pain and can overreact to pain signals. Even though there is a little or no pain, the body's response is one of exaggerated pain.
Infections
An infection could trigger the development of fibromyalgia. This may be due to the fact that the immune system becomes hyperactive when infected.
The immune system attacks healthy tissue and causes inflammation. The inflammation will then trigger fibromyalgia and lead to more intense pain.
Infections that have been linked to fibromyalgia include pneumonia, the flu, Epstein-Barr virus, and some gastrointestinal infections like Salmonella and Shigella.
Trauma
Physical and emotional trauma can also play a role in fibromyalgia. A traumatic event such as an accident, surgery, or injury can set off a chain reaction within the body that leads to chronic pain.
Emotional events can also trigger fibromyalgia. For example, significant emotional trauma, like a bad car accident or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), can trigger fibromyalgia.
It is important to note that these types of traumas may not necessarily cause fibromyalgia, but they can make it worse if someone already has fibromyalgia.
Stress
Similar to trauma, intense stress can also increase your chances of getting fibromyalgia. Stress triggers the release of hormones and changes that affect the nervous system and the immune system.
The increase in hormones can cause inflammation and pain that leads to fibromyalgia.
Symptoms

People with fibromyalgia can experience a variety of symptoms. The most common symptoms are pain, fatigue, depression, and anxiety. They may also have trouble sleeping and concentrating.
1. Pain and Stiffness All over the Body
People who suffer from fibromyalgia usually describe their pain as being all over their bodies. There can be different pain sensations like burning, stabbing, pulling, throbbing, tingling, and shooting pains.
Chronic pain is the most noticeable symptom of fibromyalgia. It can start out mild and gradually worsen over time.
Fibromyalgia pain can be felt in the muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments, nerves, and other soft tissues.
2. Fatigue and Tiredness
Fatigue is another common symptom of fibromyalgia and can last for hours at a time. People with fibromyalgia often feel tired, even after having just woken up from sleep.
Fibromyalgia can make you feel exhausted and unable to do anything without feeling fatigued. Some people with fibromyalgia find themselves without energy and constantly sleepy.
3. Depression and Anxiety

Depression and anxiety are two other common symptoms of fibromyalgia. These feelings can occur suddenly and come on separately or together.
People with fibromyalgia may experience feelings of sadness, hopelessness, worthlessness, anger, irritability, and loneliness.
4. Sleep Problems
Sleep problems are also common for people with fibromyalgia. Many people with fibromyalgia report insomnia and difficulty falling asleep.
They may also have restless legs syndrome which makes them want to move around while trying to fall asleep. They may not be able to stay asleep throughout the night and need to get up several times throughout the night.
Even after a long night's sleep, someone with fibromyalgia may still feel unrested and unrefreshed.
5. Problems with Thinking, Memory, and Concentration

People suffering from fibromyalgia may have trouble remembering names, dates, places, and more. Memory loss is one of the more common symptoms of fibromyalgia patients.
Some people with fibromyalgia also experience problems with thinking, concentration, and focus. This can lead to difficulties completing tasks and making decisions.
6. Headaches and Migraines
Fibromyalgia symptoms include headaches and migraines. They can range from mild to severe and can include migraines. Migraine headaches can be debilitating and painful, lasting anywhere from 4 to 72 hours.
7. Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet

Tingling and numbness in your hands and feet are common symptoms of fibromyalgia. It can feel like pins and needles. The symptoms are often similar to those associated with carpal tunnel syndrome and multiple sclerosis.
8. Pain in the Face or Jaw
Patients with fibromyalgia will often experience facial pain and jaw disorders, including Temporomandibular Joint Syndrome (TMJ).
The pain can be around the face, head, and neck. TMJ can lead to clicking and popping sounds with mouth movement.
9. Digestive Problems

Digestive issues are another common problem for people with fibromyalgia symptoms. Patients may experience abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, gas, and even irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms.
Fibromyalgia Risk Factors
There are a number of risk factors that increase your chances of developing fibromyalgia.
1. Sex
Women are twice as likely to develop fibromyalgia than men because they experience more hormonal changes. Hormones increase from menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause.
2. Age
Fibromyalgia can develop in children, but occurs most often in middle age. The risk of fibromyalgia increases as you get older.
As we get older, our muscles become weaker and less flexible due to lower muscle mass and bone density. Our joints start to stiffen and wear out faster as well. All these things make it easier for us to develop fibromyalgia.
3. Family History
If your parents or other close family members have been diagnosed with fibromyalgia, you are at higher risk of developing it too.
Fibromyalgia isn't hereditary, so it's not passed on from the parents to children directly. But it is still a disorder that occurs in groups within the family.
4. History of Other Conditions
Having an autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus increases your chance of developing fibromyalgia. Having thyroid disease or diabetes also raises your risk.
Other conditions that can raise your risk of fibromyalgia include TMJ, IBS, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, anxiety, and stress.
Treatments

There is no cure for fibromyalgia, so treatment options focus on managing symptoms. There are several different types of treatments available.
Medications
Many prescription and over-the-counter medications are used to treat fibromyalgia symptoms. These medications help reduce pain, improve sleep quality, and relax stiff muscles and tension.
Medications include:
- Antidepressants - Antidepressants are prescribed to relieve depression and anxiety, and improve sleep. Some antidepressants can also help control pain and stiffness.
-
Pain Relievers - These pills can be over-the-counter or prescribed to relieve pain. Examples include ibuprofen (Advil), acetaminophen (Tylenol), and naproxen sodium (Aleve).
- Anti-inflammatory - Anti-inflammatories are prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling. Inflammation is not a direct symptom of fibromyalgia, but it can cause pain and be related to conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Muscle Relaxers - Muscle relaxers are prescribed to ease tightness and spasms in muscles. They're usually taken before bedtime to help you fall asleep better.
- Antiseizure Drugs - Pregabalin (Lyrica) can help to block nerve cells from sending out pain signals. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is another drug that is prescribed to help reduce fibromyalgia symptoms.
-
Sleep Medication - Sleep medication helps you fall asleep and stay asleep. It may take some time to find the right one for you.
Natural Remedies and Therapies
When medications don't fully relieve the pain and symptoms associated with fibromyalgia, natural remedies and therapies can provide additional relief.
Natural remedies and therapies for fibromyalgia include:
- Physical Therapy - Physical therapists use exercises, stretching, massage, heat, cold, and other techniques to help relax the muscles and tension.
-
Massage Therapy - Massages are relaxing and can help reduce stress and muscle tension. That can reduce triggering symptoms and pain.
- Meditation - Meditation can help you focus your attention away from negative thoughts and feelings. It's often used by people who have chronic pain. Meditation is an effective way to calm yourself down and clear your mind. It's often used to treat insomnia and depression.
-
Yoga - Yoga focuses on breathing, relaxation, and keeping your muscles loose and flexible. It's often done at home, but yoga classes are available in many cities.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy - Cognitive behavioral therapy helps patients change their approach to stress and anxiety to reduce triggering fibromyalgia symptoms.
- Acupuncture - Acupuncture involves inserting needles into specific pressure points on the body. This therapy has been shown to help reduce pain and improve sleep.
- Acupressure - Acupressure involves applying pressure to the same pressure points as acupuncture, but without needles. It helps to stimulate the nerves and release endorphins, which can relieve the pain and make you feel more relaxed.
Acupressure is a natural, alternative therapy that originates from thousands of years of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It uses areas of the body where there are pressure points to balance energy flow throughout the body to relieve the pains and symptoms of fibromyalgia.
Some of the most common pressure points to employ self-acupressure include:
-
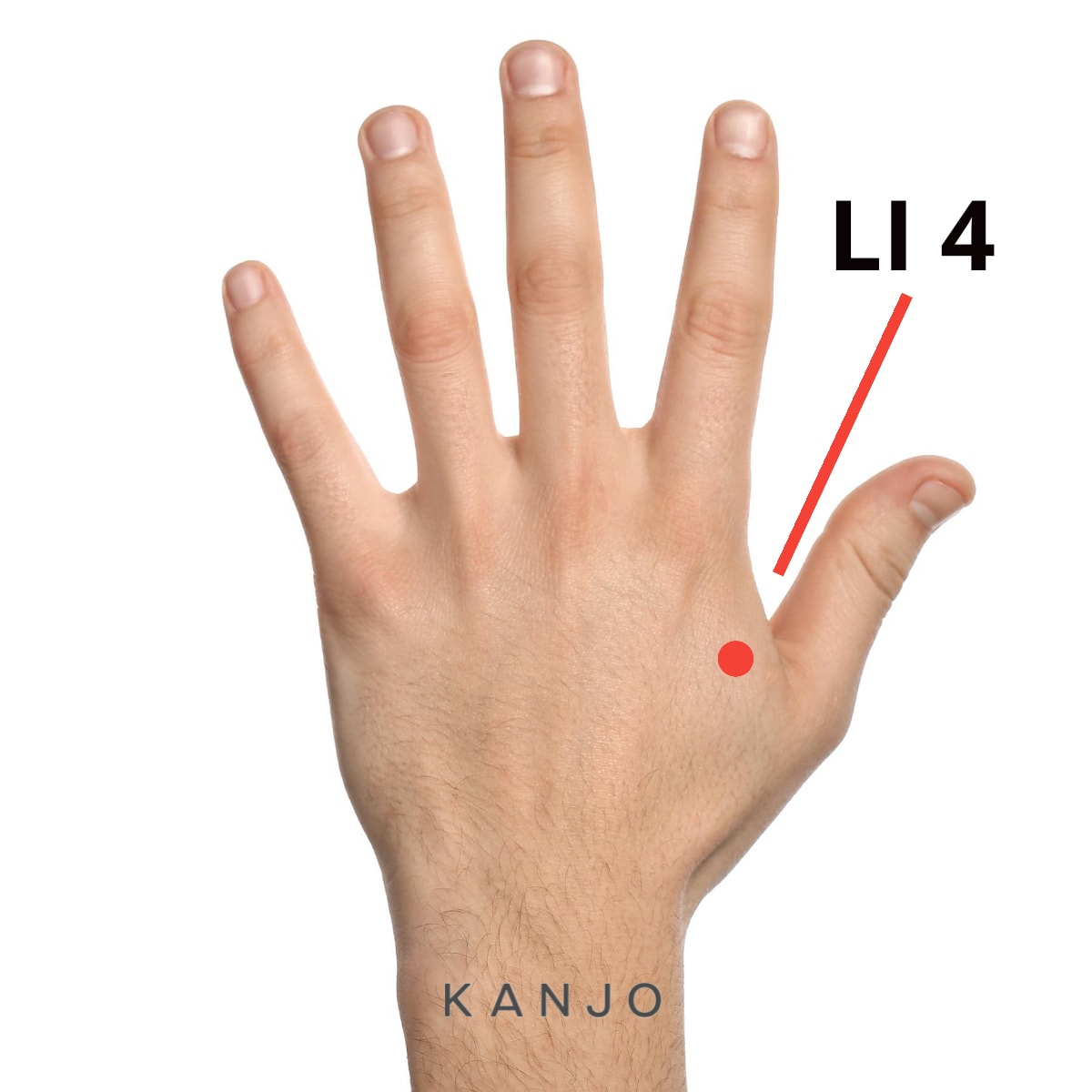
Large Intestine 4 (LI 4) - This pressure point will help to relieve headaches, neck pain, and anxiety.
-
Pericardium 6 (PC 6 or P 6) - Applying pressure to this point will help relieve anxiety, insomnia, and nausea by relaxing the mind. It can also relieve indigestion and stomach pains.

-
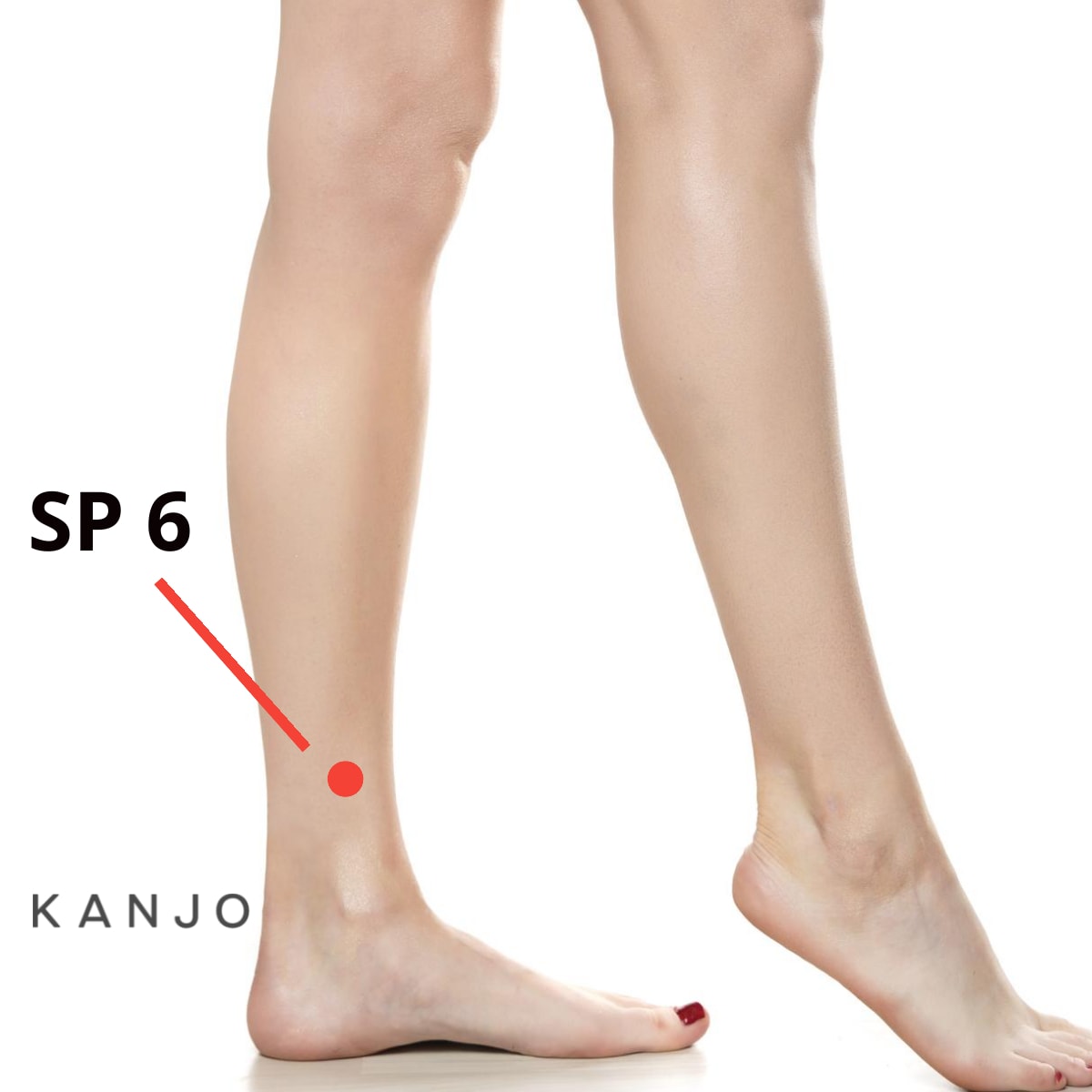
Spleen 6 (SP 6) - This acupressure point will help to relieve anxiety, stress, and insomnia. Pressure here will help to calm the mind before going to bed. It will also help relieve digestive and gastrointestinal conditions.
-
Stomach 36 (ST 36) - Firm pressure on this point will help relieve digestive issues, stomach pain, stress, and nausea.

-
Liver 3 (LV 3) - This point will help relieve abdominal distension, headaches, and pain around the eye and face.

-
Heart 7 (HT 7) - Stimulating this pressure point will offer anxiety, stress, and insomnia relief.

Fibromyalgia Summary
Fibromyalgia is a condition that can cause pain all over your body and lead to many sleepless nights. Unfortunately, there is no cure for fibromyalgia, but a variety of treatments are available to help manage its symptoms.
Talk to your doctor about what combination of treatment options may be right for you. You might try some of these therapies alone or together with other medications or complementary therapies.
Sources:
- CDC: https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/fibromyalgia.htm
- Healthline: https://www.healthline.com/health/fibromyalgia
- Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/fibromyalgia/symptoms-causes/syc-20354780
- Medical News Today: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/147083
